The Gateway Chronicles: Teaching Envoy to Talk to Your App
Overview
Envoy Gateway is a Kubernetes-native API gateway built on top of Envoy Proxy which has functions for network and traffic management. It’s designed to work seamlessly with the Kubernetes Gateway API and takes a batteries-included approach—offering built-in support for authentication, authorization, rate limiting, CORS handling, header manipulation, and more. These capabilities are exposed through familiar Kubernetes-style APIs, letting you fully tap into Envoy’s power without needing complex configurations. In essence, the Gateway API provides a standard interface. Envoy Gateway adds production-grade capabilities to that interface, bridging the gap between simplicity and power while keeping everything Kubernetes-native.
Correlation Gateway API with Envoy
The relationship between these custom resources and the standard resources of the Gateway API is illustrated in the diagram below: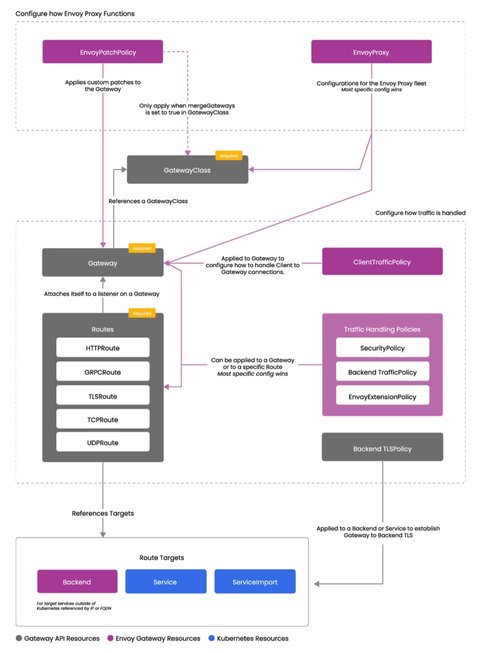
Envoy Gateway Parts
Envoy Gateway is a system made up of two main parts:
- A
data plane, which handles the actual network traffic - A
control plane, which manages and configures the data plane
Use Cases
Use The Gateway API to:
- Define how external traffic enters and is routed within your cluster
- Configure HTTP(S), TLS, and TCP traffic routing in a standardized, Kubernetes-native way
- Apply host-based, path-based, and header-based routing rules using HTTPRoute
- Terminate TLS at the edge using Gateway TLS configuration
- Separate responsibilities between infrastructure and application teams through role-oriented resource design
- Improve portability and consistency across different gateway implementations
Objectives
In this article, we’ll walk through the step-by-step installation of the Envoy Gateway on a local Kubernetes cluster and create a sample mechanism to route the traffic to the sample app.
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster
- Kubectl
- Helm
Installation
Install the Gateway API CRDs and Envoy Gateway:
helm install eg oci://docker.io/envoyproxy/gateway-helm --version v1.6.0 -n envoy-gateway-system --create-namespaceWait for Envoy Gateway to become available:
kubectl wait --timeout=5m -n envoy-gateway-system deployment/envoy-gateway --for=condition=AvailableInstall the GatewayClass, Gateway, HTTPRoute and example app:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
name: eg
spec:
controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: eg
spec:
gatewayClassName: eg
listeners:
- name: http
protocol: HTTP
port: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: backend
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: backend
labels:
app: backend
service: backend
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
selector:
app: backend
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: backend
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: backend
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: backend
version: v1
spec:
serviceAccountName: backend
containers:
- image: gcr.io/k8s-staging-gateway-api/echo-basic:v20231214-v1.0.0-140-gf544a46e
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: backend
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: backend
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: eg
hostnames:
- "www.corenux-test.com"
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: backend
port: 3000
weight: 1
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /Testing the Configuration
Without LoadBalancer Support
Get the name of the Envoy service created the by the example Gateway:
export ENVOY_SERVICE=$(kubectl get svc -n envoy-gateway-system --selector=gateway.envoyproxy.io/owning-gateway-namespace=default,gateway.envoyproxy.io/owning-gateway-name=eg -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')Port forward to the Envoy service:
kubectl -n envoy-gateway-system port-forward service/${ENVOY_SERVICE} 8888:80 &Curl the example app through Envoy proxy:
curl --verbose --header "Host: www.corenux-test.com" http://localhost:8888/getOutput
* Host localhost:8888 was resolved.
* IPv6: ::1
* IPv4: 127.0.0.1
* Trying [::1]:8888...
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8888
> GET /get HTTP/1.1
> Host: www.corenux-test.com
> User-Agent: curl/8.7.1
> Accept: */*
>
* Request completely sent off
Handling connection for 8888
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< content-type: application/json
< x-content-type-options: nosniff
< date: Mon, 17 Nov 2025 11:21:26 GMT
< content-length: 471
<
{
"path": "/get",
"host": "www.corenux-test.com",
"method": "GET",
"proto": "HTTP/1.1",
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"User-Agent": [
"curl/8.7.1"
],
"X-Envoy-External-Address": [
"127.0.0.1"
],
"X-Forwarded-For": [
"10.10.10.2"
],
"X-Forwarded-Proto": [
"http"
],
"X-Request-Id": [
"0aa2f6d7-f94b-4ab3-8429-aec5beec0cda"
]
},
"namespace": "default",
"ingress": "",
"service": "",
"pod": "backend-77d4d5968-r4cxc"
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
}Check Envoy Default Gateway Logs
{
":authority":"www.corenux-test.com",
"bytes_received":0,
"bytes_sent":471,
"connection_termination_details":null,
"downstream_local_address":"127.0.0.1:10080",
"downstream_remote_address":"127.0.0.1:33138",
"duration":2,
"method":"GET",
"protocol":"HTTP/1.1",
"requested_server_name":null,
"response_code":200,
"response_code_details":"via_upstream",
"response_flags":"-",
"route_name":"httproute/default/backend/rule/0/match/0/www_corenux-test_com",
"start_time":"2025-11-17T11:21:26.178Z",
"upstream_cluster":"httproute/default/backend/rule/0",
"upstream_host":"10.10.10.32:3000",
"upstream_local_address":"10.10.10.2:36304",
"upstream_transport_failure_reason":null,
"user-agent":"curl/8.7.1",
"x-envoy-origin-path":"/get",
"x-envoy-upstream-service-time":null,
"x-forwarded-for":"10.10.10.2",
"x-request-id":"0aa2f6d7-f94b-4ab3-8429-aec5beec0cda"
}Results
In this quickstart, you have:
- Installed Envoy Gateway
- Deployed a backend service, and a gateway
- Configured the gateway using Kubernetes Gateway API resources Gateway and HTTPRoute to direct incoming requests over HTTP to the backend service.